The Adrenal Glands and their function
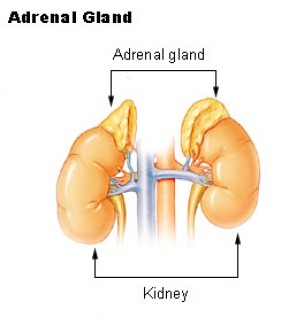
The adrenal glands are a pair of endocrine glands each located on the top of one of the kidneys. Each gland consists of the outer cortex (which makes up 90 percent of the gland) and the inner medulla. Both parts secrete hormones that regulate the functions of other organs and systems into the bloodstream. The adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline (or epinephrine) and noradrenaline (or norepinephrine), which have similar actions. These hormones, which are neurotransmitters, regulate activity in the sympathetic nervous system. They control automatic functions such as blood vessel constriction, heart rate, gastrointestinal movements, pupil dilation, and glucose metabolism. When hormone secretion by the adrenal medulla is increased, the blood vessels constrict, the heart accelerates, gastrointestinal movements diminish, and glucose is released into the bloodstream. These events occur in emergencies and are physiologic responses that help the individual survive.
The adrenal cortex secretes three principal types of steroid hormones: glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), and androgens. Adrenal steroid hormones regulate metabolism of carbohydrate, fat, and protein; neuromuscular function; salt and water metabolism; sexual function; resistance to infection and other stresses.
Information taken from: Grolier Online Encyclopedia
Guoth, Maria. "adrenal gland." Grolier Multimedia Encyclopedia. 2008. Grolier Online. 29 Oct. 2008 <http://gme.grolier.com/cgi-bin/article?assetid=0002940-0>.
Adrenaline/Epinepherine
The adrenal glands are a pair of endocrine glands each located on the top of one of the kidneys. Each gland consists of the outer cortex (which makes up 90 percent of the gland) and the inner medulla. Both parts secrete hormones that regulate the functions of other organs and systems into the bloodstream. The adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline (or epinephrine) and noradrenaline (or norepinephrine), which have similar actions. These hormones, which are neurotransmitters, regulate activity in the sympathetic nervous system. They control automatic functions such as blood vessel constriction, heart rate, gastrointestinal movements, pupil dilation, and glucose metabolism. When hormone secretion by the adrenal medulla is increased, the blood vessels constrict, the heart accelerates, gastrointestinal movements diminish, and glucose is released into the bloodstream. These events occur in emergencies and are physiologic responses that help the individual survive.
The adrenal cortex secretes three principal types of steroid hormones: glucocorticoids (cortisol), mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), and androgens. Adrenal steroid hormones regulate metabolism of carbohydrate, fat, and protein; neuromuscular function; salt and water metabolism; sexual function; resistance to infection and other stresses.
Information taken from: Grolier Online Encyclopedia
Guoth, Maria. "adrenal gland." Grolier Multimedia Encyclopedia. 2008. Grolier Online. 29 Oct. 2008 <http://gme.grolier.com/cgi-bin/article?assetid=0002940-0>.
Diseases and disorders
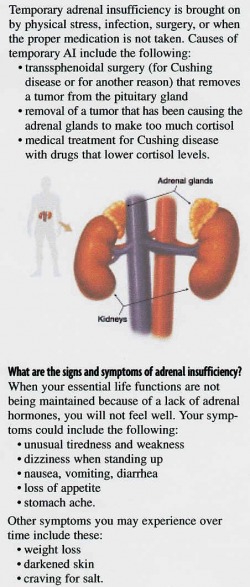
1. Addison disease is a disease in which hormone secretion by the adrenal cortex is impaired. This disease can be treated with the administration of synthetic cortical hormones.
2. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) deficiency is a genetic disorder in which affected patients cannot synthesize norepinephrine and epinephrine
Excessive amounts of Adrenaline can cause erratic heart beat.
Citations:
Guoth, Maria. "adrenal gland." Grolier Multimedia Encyclopedia. 2008. Grolier Online. 29 Oct. 2008 <http://gme.grolier.com/cgi-bin/article?assetid=0002940-0>.
External Links
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adrenal_gland
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epinephrine
http://go.grolier.com/
